Choosing the best online business model is a crucial first step for any aspiring entrepreneur. The right model aligns with your skills, resources, and market opportunities, setting the foundation for a successful online business. This comprehensive guide explores various online business models, helping you identify the perfect fit for your entrepreneurial journey. We’ll cover everything from e-commerce and dropshipping to affiliate marketing, online courses, and subscription services. Understanding the nuances of each model, including the startup costs, profit potential, and required time commitment, is essential for making an informed decision.
Navigating the diverse landscape of online business models can feel overwhelming. This article simplifies the process by providing a clear and concise overview of the most popular options. We’ll delve into the pros and cons of each model, allowing you to weigh the advantages and disadvantages based on your individual circumstances. By the end of this guide, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge and insights necessary to confidently select the best online business model to launch your successful online venture and achieve your business goals.
The Importance of a Solid Business Model
A robust business model is the cornerstone of any successful venture. It provides a clear framework for how a company creates, delivers, and captures value. This framework encompasses key aspects such as the target customer, the value proposition offered, the revenue generation mechanisms, and the cost structure. A well-defined business model provides a roadmap for sustainable growth and profitability, allowing businesses to attract investment, allocate resources effectively, and navigate the competitive landscape.
Developing a solid business model requires a deep understanding of the market and the needs of the target audience. It involves identifying a unique value proposition that differentiates the business from competitors. This proposition can take many forms, such as offering superior product quality, providing exceptional customer service, or implementing innovative technology. A strong value proposition attracts customers and builds brand loyalty, driving revenue and market share growth.
Ultimately, a successful business model translates vision into actionable strategy. It aligns the organization’s activities with its overarching goals, fostering a cohesive and efficient operational framework. This alignment is crucial for long-term success, enabling the business to adapt to changing market conditions and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Popular Models for Online Entrepreneurs

Several business models have proven successful for online entrepreneurs. One popular option is e-commerce, where businesses sell products directly to consumers through an online store. This model can involve various approaches, including dropshipping, where a third party handles inventory and shipping, or wholesaling, where the business manages its own stock. Another successful model is content creation, where entrepreneurs generate valuable content, such as videos, blog posts, or online courses, and monetize it through advertising, subscriptions, or sponsorships. Finally, the affiliate marketing model allows individuals to earn commissions by promoting other companies’ products or services on their websites or social media platforms.
Subscription services have also gained significant traction in recent years. This model offers customers recurring access to products or services in exchange for a regular fee. Examples include software subscriptions, streaming services, and curated subscription boxes. Subscription models offer predictable revenue streams and foster strong customer relationships. Another increasingly popular model is the freemium approach, which offers a basic version of a product or service for free while charging for premium features or enhanced functionality. This allows businesses to attract a large user base and convert a portion of them to paying customers.
Selecting the right model depends on several factors, including the entrepreneur’s skills, resources, and target market. Careful consideration of the target audience, the competitive landscape, and the entrepreneur’s own strengths is crucial for success in the competitive online business environment. Proper planning and execution are essential regardless of the chosen model.
Affiliate, Dropshipping, and Print-on-Demand
Affiliate marketing is a performance-based marketing strategy where businesses reward affiliates for each customer brought in by the affiliate’s own marketing efforts. Affiliates earn a commission for driving traffic and sales through unique referral links. This model requires minimal upfront investment from the affiliate, focusing primarily on marketing and promotion. Success relies heavily on building trust with an audience and recommending relevant products or services.
Dropshipping is a retail fulfillment method where a store doesn’t keep the products it sells in stock. Instead, when a store sells a product, it purchases the item from a third-party supplier who then ships it directly to the customer. This eliminates the need for inventory management and significantly reduces startup costs for the retailer. The focus for dropshippers is on marketing, customer service, and selecting reliable suppliers.
Print-on-demand is a product fulfillment method where items are printed only as they are ordered. This allows for a wide variety of customizable products and eliminates the need for large upfront inventory investments. Designs are printed onto products like t-shirts, mugs, and phone cases as orders come in, then shipped directly to the customer. This model offers a low-risk entry point for entrepreneurs interested in selling customized merchandise.
Subscription and SaaS Revenue Streams
Subscription and Software as a Service (SaaS) revenue streams represent a powerful model for recurring income. Subscriptions involve customers paying a recurring fee for access to a product or service, often delivered digitally. This provides a predictable revenue stream for businesses and allows for ongoing customer relationships. SaaS, a subset of the subscription model, delivers software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for local installations and offering scalable solutions for businesses of all sizes.
Key benefits of this revenue model include predictable revenue, which facilitates financial planning and investment. It fosters customer loyalty through ongoing engagement and value delivery. It also allows for scalability as digital delivery reduces marginal costs associated with serving additional customers. Furthermore, these models often incorporate usage-based pricing tiers, allowing businesses to cater to different customer needs and maximize revenue potential.
Several common examples of subscription/SaaS offerings exist across diverse industries. These include streaming services like Netflix or Spotify, cloud storage solutions like Dropbox or Google Drive, and business software applications like Salesforce or Slack. The widespread adoption of these models highlights their effectiveness in generating recurring revenue and delivering value to customers.
Service-Based vs Product-Based Online Models
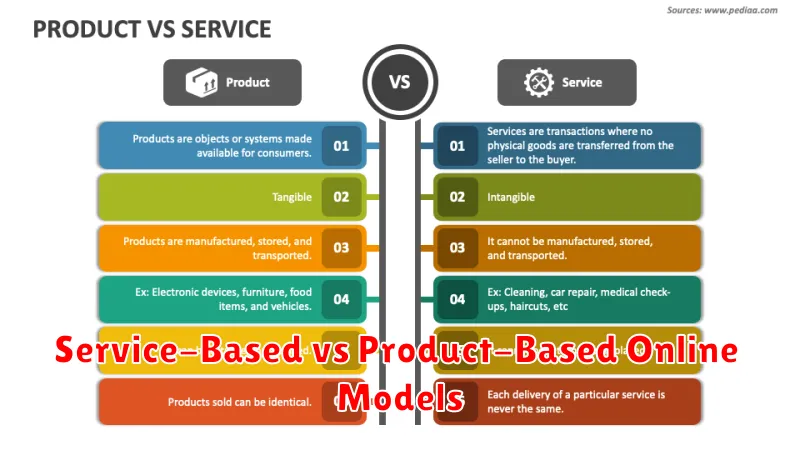
Service-based online businesses primarily offer intangible services delivered digitally or facilitated through online platforms. These can include consulting, coaching, online education, graphic design, virtual assistance, and software development. Key characteristics of service-based models are the emphasis on expertise and personalized solutions. Revenue generation typically involves charging hourly rates, project fees, or subscription fees for ongoing services. Scaling a service-based business often requires hiring more service providers or leveraging technology to automate certain aspects of service delivery.
Product-based online businesses focus on selling physical or digital products through e-commerce platforms, online marketplaces, or their own websites. These products can range from handmade crafts and clothing to software, ebooks, online courses, and digital art. The core focus of these models is on product development, marketing, and efficient fulfillment and delivery. Revenue is generated through direct sales, with profits depending on factors like pricing strategy, production costs, and sales volume. Scalability for product-based businesses often involves optimizing production processes, inventory management, and marketing strategies.
Choosing between these two models depends on several factors, including your skills, resources, and target market. Some businesses even adopt a hybrid approach, combining elements of both service and product offerings to diversify revenue streams and cater to a wider audience. Careful consideration of your long-term goals and the specific demands of each model is crucial for online business success.
Assessing Scalability and Profit Margins
Scalability refers to a business’s ability to increase output and revenue without a proportional increase in costs. Analyzing scalability requires evaluating factors like production capacity, market demand, and the efficiency of operational processes. Businesses with high scalability potential can significantly increase profits as they grow, benefiting from economies of scale. Conversely, businesses with limited scalability may struggle to maintain profit margins as they expand, facing rising costs and diminishing returns.
Profit margins represent the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting all expenses. Healthy profit margins are crucial for long-term sustainability and reinvestment. Assessing profit margins involves calculating key metrics like gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin. Understanding these metrics allows businesses to identify areas for improvement, optimize pricing strategies, and ultimately enhance profitability.
Evaluating scalability and profit margins together provides a comprehensive view of a business’s financial health and growth potential. A scalable business model combined with strong profit margins indicates a promising investment opportunity. However, it’s important to remember that high scalability doesn’t always guarantee high profitability. Careful planning and execution are essential to leverage scalability and translate it into sustained financial success.
Real-Life Examples of Each Model

Several business models exist, each with unique characteristics. The Business-to-Consumer (B2C) model involves businesses selling directly to individual consumers. Examples include retail stores like Target and Walmart, e-commerce platforms like Amazon, and streaming services like Netflix. These businesses focus on high-volume transactions and often emphasize marketing and customer experience.
Business-to-Business (B2B) models involve transactions between businesses. Software companies like Salesforce, marketing agencies, and raw material suppliers fall into this category. These businesses often prioritize building long-term relationships and offer specialized products or services tailored to the needs of other businesses. Sales cycles tend to be longer and involve more complex decision-making processes.
The Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) model connects individual buyers and sellers. Platforms like eBay, Craigslist, and Facebook Marketplace facilitate these transactions. C2C businesses primarily provide a platform for exchange and often implement systems for user feedback and dispute resolution. This model relies on individual users driving the marketplace activity.
Speed is crucial in today’s competitive market. Utilizing the right tools can significantly decrease development time and get your product to market faster. Rapid prototyping tools like Figma and Adobe XD allow for quick design iteration and user feedback. For development, low-code/no-code platforms such as Webflow and Bubble enable faster building of functional applications with minimal coding. Finally, continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines automate testing and deployment, streamlining the release process.
Choosing the right toolset depends heavily on your project’s specific needs. Consider the complexity of your project, your team’s technical skills, and your budget. For simple web applications, a no-code platform might be sufficient. For more complex projects requiring custom functionality, a robust coding framework combined with CI/CD is more suitable. Evaluating your requirements upfront is key to selecting the most effective tools.
Once your tools are chosen, prioritize effective collaboration within your team. Project management tools like Trello or Asana can help keep everyone organized and on track. Clear communication channels and regular feedback loops are also essential. By combining the right tools with strong teamwork, you can dramatically accelerate your build and launch process.
Testing Your Model Before Scaling
Before scaling your machine learning model, thorough testing is crucial to ensure its performance and reliability. This involves evaluating the model on a representative dataset that wasn’t used during training. This helps to identify potential issues like overfitting, where the model performs well on training data but poorly on new data. Additionally, testing allows you to assess key performance indicators (KPIs) such as accuracy, precision, and recall, which provide insights into the model’s effectiveness in real-world scenarios.
Beyond performance metrics, testing should also consider the model’s robustness and stability. This means evaluating its behavior with various input data, including edge cases and potentially corrupted data. Testing for robustness helps uncover vulnerabilities and ensures the model can handle unexpected inputs gracefully. Furthermore, stability testing is essential, verifying consistent performance over time and across different environments. This ensures the model remains reliable even with changes in data distribution or infrastructure.
Finally, consider the practical implications of scaling. Testing should encompass the model’s integration with other systems, its computational requirements, and its potential impact on existing workflows. Addressing these aspects beforehand can prevent unexpected issues and facilitate a smooth transition to a larger-scale deployment. By focusing on thorough testing, you can mitigate risks, ensure performance, and pave the way for a successful scaling process.
How to Avoid Common Pitfalls
Planning is crucial to avoid pitfalls. Clearly define your goals and objectives. A well-defined plan helps anticipate potential problems and develop strategies to overcome them. Break down large tasks into smaller, manageable steps. This allows for better tracking of progress and identification of potential issues early on.
Communication is key to successful execution. Maintain open and transparent communication with all stakeholders. Regular updates and feedback sessions can help identify and address potential roadblocks before they become major problems. Ensure that everyone is on the same page and understands their roles and responsibilities.
Risk assessment is an essential part of any project. Identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies. This proactive approach can significantly reduce the likelihood of encountering pitfalls. Contingency planning is also crucial. Having backup plans in place can help you navigate unexpected challenges and keep your project on track.

